Are you new to the world of sewing? Have you been wanting to learn how to sew but don’t know where to start? If so, then the first step is understanding what a sewing machine is and how it works. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the basics of a sewing machine and provide some helpful tips on selecting the one that’s right for you.
A sewing machine is a machine used to stitch fabric and other materials together with thread. Sewing machines were invented during the first industrial revolution. The goal of this was to reduce the amount of manual sewing work done in clothing and textile factories.
Today’s sewing machines are computerized and can be used to embroider, quilt, and carry out a broad range of sewing and decorative stitching.
Table of Contents
History of Sewing Machines
The history of the sewing machine dates back to 1755 when Charles Weisenthal, a German immigrant, took out a patent for a needle to be used for mechanical sewing. But the first sewing machine that was mass-produced was designed and made by French tailor Barthelemy Thimonnier in 1830. Thimonnier’s machine used only one thread and was met with much opposition from local tailors who were afraid of being replaced by the machine.
In 1842, the first record of a sewing machine invention was granted in the Patent-office Reports. The machine was improved to make a variety of the same machine. But, in 1846, Elias Howe who was from Massachusetts but living in Connecticut, patented the sewing machine. That truly set off a technological, industrial, and social revolution. Howe’s invention made sewing faster and easier than it had been before, and it became a necessary tool for businesses in the textile industry.

In the following years, Howe’s invention was improved upon and further developed by other inventors such as Isaac Singer and Allen B. Wilson. Singer’s machine was the first to utilize a foot pedal, making it easier to use. Wilson’s machine was the first to incorporate an overlock stitch.
By the early 20th century, the sewing machine had become an essential part of the garment industry and has remained so ever since. Today, sewing machines are used in a variety of industries, from making clothing to creating furniture and other items. They are also used for a variety of craft and hobby projects.
Types of Sewing Machines By How They Work
Manual sewing machines: These machines may look like regular sewing machines, but they don’t need electricity to function. Instead, they use a foot treadle to power the machine.

Mechanical Sewing Machine: Mechanical sewing machines are operated machines that use a hand crank to power the needle. They are usually smaller, more affordable, and ideal for basic sewing tasks. And most mechanical sewing machines are powered by electricity.
Electronic sewing machine: You can program it to do specific tasks like creating a buttonhole or attaching a zipper. They may also be programmable, allowing users to select from a range of stitches and settings. They are often computerized and can be used to create intricate designs and patterns.

Computerized Sewing Machine: this is an advanced type of sewing machine that uses computer technology and a wide range of features to help make sewing easier and more efficient. Computerized sewing machines are ideal for quilting, embroidery, or other intricate projects.

If you are interested in learning more about choosing a sewing machine, I recommend reading my blog post on how to choose a sewing machine.
Parts of a Sewing Machine
These are essential parts to a sewing machine:
- Bobbin: The bobbin is the spool of thread that is held in the bobbin case underneath the needle plate.
- Bobbin Case: The bobbin case holds the bobbin in place. It is typically located underneath the needle plate.
- Needle Plate: The needle plate is the metal plate that covers the bobbin case. It has a hole in the center to allow the needle to pass through.
- Needle: The needle is the sharp metal piece that passes through the fabric and thread to create stitches.
- Thread Take-Up Lever: It’s a metal arm that helps guide the thread from the spool to the needle.
- Feed Dogs: The feed dogs are the metal teeth located underneath the needle plate that help move the fabric along as the stitch is being created.
- Foot Pedal: It is the lever at the base of the machine that is used to control the speed of the needle.
- Stitch Length Dial: The stitch length dial is used to adjust the length of the stitches.
- Bobbin Winder: The bobbin winder is used to fill the bobbin with thread.
- Pressure Foot: It is the metal plate at the front of the machine that holds the fabric in place while stitching.
- Stitch Selector: Controls the type of stitch used.
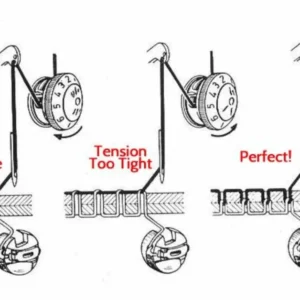
- Thread Tension Dial: A knob used to control the tension of the thread.
- Spool Pin: Used to hold the spool of thread.

Conclusion
That’s it for our quick guide to sewing machines. From the basics of what a sewing machine is to understanding the different types, we’ve covered it all.
If you are looking for a detailed breakdown of the top sewing machines in 2023, then look at our guide on the best sewing machines on the market now.
Finally, If you have any questions or need some help getting started, don’t hesitate to reach out. We’re here for you!